JAVA:作业一
1、 计算多项式1!+2!+3!…+n!,当多项式之和超过10000时停止,并输出累加之和以及n的值。
package com;
public class aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int n = 0;
while (sum<10000)
{
n+=1;
sum=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int ans = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
ans *= j;
}
sum += ans;
}
}
System.out.println("累加和sum:"+ sum);
System.out.println("对应的n:"+ n);
}
}
2、 从标准输入端输入一个字符,判断字符是数字、还是西文字母还是其他的字符。
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个字符:");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
char ans = scan.next().charAt(0);
if (ans>= 'a' && ans<= 'z' || ans>= 'A' && ans<= 'Z' )
{
System.out.println(ans+ " 是西文字母" );
}
else if (ans>= '0' &&ans<= '9' )
{
System.out.println(ans+ " 是数字" );
}
else
{
System.out.println(ans+ " 是其他字符" );
}
}
}
3、 利用辗转相除法(欧几里得算法)求两个正整数的最大公约数。
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入两个正整数:");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
if (a < b) {
int c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
System.out.println(a + " 和 " + b + " 的最大公约数为:");
int ans;
while (b != 0) {
ans = a % b;
a = b;
b = ans;
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}
4、 假设一个数在1000到1100之间,那除以3结果余2,;除以5结果余3,;除以7结果余2(中国剩余定理),求此数。
package com;
public class aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int ans;
for (ans = 1000; ans <= 1100; ans++) {
if (ans % 3 == 2 && ans % 5 == 3 && ans % 7 == 2)
break;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
5、 小球从100米高度自由落下,每次触地后反弹到原来高度的一半,求第10次触地时经历的总路程以及第10次反弹高度。
package com;
public class aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double h = 100, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
ans += h;
h = h / 2;
ans += h;
}
System.out.println("第10次触地时经历的总路程:" + ans);
System.out.println("第10次反弹高度:" + h);
}
}
JAVA:作业二
1 读程序,写结果
class A {
public String Show(D obj) { return ("A and D"); }
public String Show(A obj) { return ("A and A"); }
}
class B extends A {
public String Show(B obj) { return ("B and B"); }
public String Show(A obj) { return ("B and A"); }
}
class C extends B {
public String Show(C obj) { return ("C and C"); }
public String Show(B obj) { return ("C and B"); }
}
class D extends B {
public String Show(D obj) { return ("D and D"); }
public String Show(B obj) { return ("D and B"); }
}
public class mainTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println(a1.Show(b));
System.out.println(a1.Show(c));
System.out.println(a1.Show(d));
System.out.println(a2.Show(b));
System.out.println(a2.Show(c));
System.out.println(a2.Show(d));
System.out.println(b.Show(b));
System.out.println(b.Show(c));
System.out.println(b.Show(d));
}}题目分析:
A a1 = new A();父类引用实例化父类对象,调用A中的方法,但是没有B类作为参数,因此以参数类型为A的方法优先调用,打印出A and A。
A a1 = new A();父类引用实例化父类对象,调用A中的方法,但是没有C类作为参数,因此以参数类型为A的方法优先调用,打印出A and A。
A a1 = new A();父类引用实例化父类对象,调用A中参数类型为D的方法,打印结果是A and D。
A a2 = new B();父类引用a2指向子类对象,向上转型,即调用父类的方法,当父类中的方法被子类重写后,就需要调用重写后的方法,注:a2的类型是A。
A中show方法的参数没有是B的,但是参数b为A类的子类对象,向上转型,调用show(A obj),但show(A obj)已经被重写为return (“B and A”)。打印出B and A。
同理4,打印出B and A。
同理4,打印出A and D。
B b = new B();b为B类,调用b.show()方法,B类的show方法有继承的show(D obj)和本身的show(B obj)、show(A obj)。
调用show(B obj),打印出B and B。
向上转型,调用show(B obj),打印出B and B。
调用show(D obj),打印出A and D。
最终答案:
A and A
A and A
A and D
B and A
B and A
A and D
B and B
B and B
A and D 2 读程序,写结果
class Base {
private String name = "base";
public Base() {
tellName();}
public void tellName() {
System.out.println("Base tell name: " + name); }
}
public class Dervied extends Base {
private String name = "dervied";
public Dervied() {
tellName();}
public void tellName() {
System.out.println("Dervied tell name: " + name);}
public static void main(String[] args){
new Dervied();
}}题目分析:
子类调用父类构造器完成初始化,在父类里调用了tellName(),但这个方法被子类重写了,输出子类成员变量name的值,此时name在子类的值还是null,并未赋值:dervied,所以,输出了null。
成员变量是在进入构造器之后被赋值:dervied;输出dervied。
最终答案:
Dervied tell name: null
Dervied tell name: dervied 3 生成动物
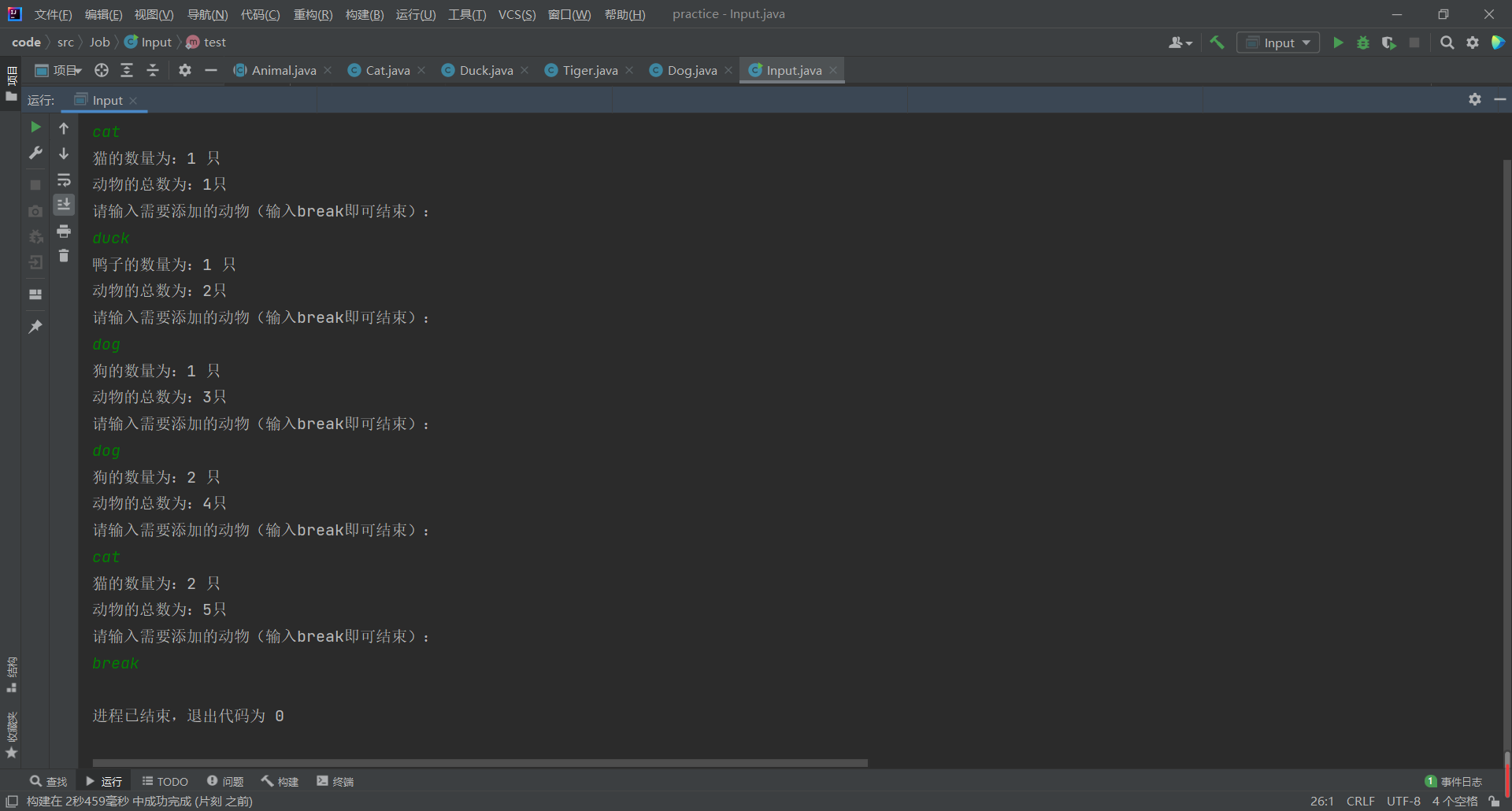
1 )循环通过标准输入端输入需要生成的动物,当遇到结束标志,则结束程序运行。
结束标准为:break
2 )每次生成动物,通过标准输出端显示动物的信息。
3 )动物的信息包括:目前所有动物的总数,当前这一类动物的总数。
4 )整个程序结构用工厂模式设计,保证将来动物园有新的动物加入时,程序可扩展。
package Job;
public abstract class Animal {
public static int count_all = 0;
public void sum() {
count_all = count_all + 1;
System.out.println("动物的总数为:" + count_all + "只");
}
}
package Job;
public class Cat extends Animal {
private static int count_cat = 0;
public void set_cat() {
count_cat = count_cat + 1;
System.out.println("猫的数量为:" + count_cat + " 只");
super.sum();
}
}
package Job;
public class Duck extends Animal {
private static int count_duck = 0;
public void set_duck() {
count_duck = count_duck + 1;
System.out.println("鸭子的数量为:" + count_duck + " 只");
super.sum();
}
}
package Job;
public class Dog extends Animal {
private static int count_dog = 0;
public void set_dog() {
count_dog = count_dog + 1;
System.out.println("狗的数量为:" + count_dog + " 只");
super.sum();
}
}
package Job;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Input {
public static void test() {
Cat cat_d = new Cat();
Duck duck_d = new Duck();
Tiger tiger_d = new Tiger();
Dog dog_d = new Dog();
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入需要添加的动物(输入break即可结束):");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scan.next();
int flag = 0;
switch (name) {
case "cat":
cat_d.set_cat();
flag = 0;
break;
case "duck":
duck_d.set_duck();
flag = 0;
break;
case "tiger":
tiger_d.set_tiger();
break;
case "dog":
dog_d.set_dog();
break;
case "break":
flag = 1;
break;
default:
System.out.println("请输入正确的动物名称!");
flag = 0;
break;
}
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
}
JAVA:作业三
1 学生管理系统
用泛型List管理学生信息,学生对象信息为
姓名 学号 年龄 专业
对学生列表完成:添加,删除,查找,全部显示操作。
学生类
package stu_manage;
public class Student {
private String name;
private String stu_id;
private String age;
private String stu_pro;
public Student(){}
public Student(String stu_id, String name, String age, String stu_pro) {
this.name = name;
this.stu_id = stu_id;
this.age = age;
this.stu_pro = stu_pro;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setStu_id(String stu_id) {
this.stu_id = stu_id;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setStu_pro(String stu_pro) {
this.stu_pro = stu_pro;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getStu_id() {
return stu_id;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getStu_pro() {
return stu_pro;
}
}
主类
package stu_manage;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Stu_manager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<Student>();
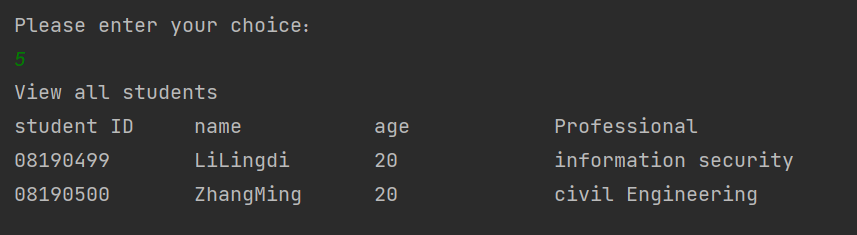
Student new_1 = new Student("08190499", "LiLingdi", "20", "information security");
Student new_2 = new Student("08190500", "ZhangMing", "20", "civil Engineering");
arrayList.add(new_1);
arrayList.add(new_2);
while (true) {
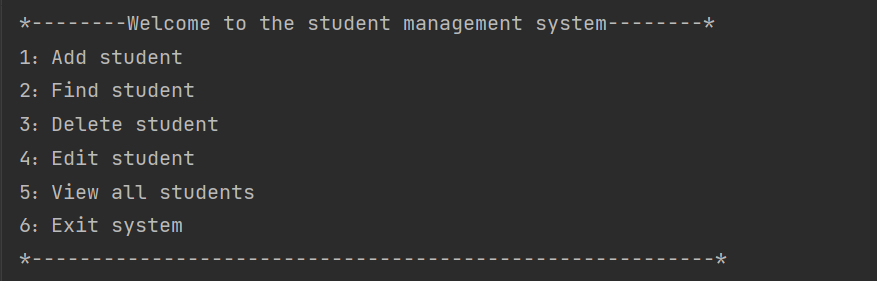
System.out.println("*--------Welcome to the student management system--------*");
System.out.println("1:Add student");
System.out.println("2:Find student");
System.out.println("3:Delete student");
System.out.println("4:Edit student");
System.out.println("5:View all students");
System.out.println("6:Exit system");
System.out.println("*---------------------------------------------------------*");
System.out.println("Please enter your choice:");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = scan.nextLine();
switch (line) {
case "1":
System.out.println("Add student");
addStudent(arrayList);
break;
case "2":
System.out.println("Find student");
findStudent(arrayList);
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("Delete student");
deleteStudent(arrayList);
break;
case "4":
System.out.println("Edit student");
updateStudent(arrayList);
break;
case "5":
System.out.println("View all students");
findAllStudent(arrayList);
break;
case "6":
System.out.println("Thanks for using");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
//添加学生信息
public static void addStudent(ArrayList<Student> arrayList) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String stu_id;
while (true) {
System.out.println("Please enter student ID:");
stu_id = sc.nextLine();
boolean flag = isUsed(arrayList, stu_id);
if (flag) {
System.out.println("The student ID you entered is used, please re-enter");
} else {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Please enter the student's name:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the age of the student:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the student's major:");
String stu_pro = sc.nextLine();
Student s = new Student();
s.setStu_id(stu_id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setStu_pro(stu_pro);
arrayList.add(s);
System.out.println("Add student successfully");
System.out.println();
}
//判断学号是否存在
public static boolean isUsed(ArrayList<Student> arrayList, String stu_id) {
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student s = arrayList.get(i);
if (s.getStu_id().equals(stu_id)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
//查找某一个学生
public static void findStudent(ArrayList<Student> arrayList) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the student ID you are looking for:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student s = arrayList.get(i);
if (s.getStu_id().equals(id)) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("The entered student number does not exist, please enter the correct student number");
} else {
System.out.println("Found student successfully!");
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.format("%-15s", "student ID") + String.format("%-15s", "name") + String.format("%-15s", "age") + String.format("%-15s", "Professional"));
Student s = arrayList.get(index);
System.out.println(String.format("%-15s", s.getStu_id()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getName()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getAge()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getStu_pro()));
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
//删除学生
public static void deleteStudent(ArrayList<Student> arrayList) {
if (arrayList.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("No student information, please add a student first, and then delete it!");
return;
}
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please enter the student ID of the student to be deleted:");
String stu_id = sc.nextLine();
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student s = arrayList.get(i);
if (s.getStu_id().equals(stu_id)) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("The entered student number does not exist, please enter the correct student number");
} else {
arrayList.remove(index);
System.out.println("Successfully deleted student");
}
System.out.println();
}
//修改学生信息
public static void updateStudent(ArrayList<Student> arrayList) {
if (arrayList.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("No student information, please add student information first");
return;
}
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter student ID:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
int inde = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student student = arrayList.get(i);
if (student.getStu_id().equals(id)) {
inde = i;
break;
}
}
//判断学号是否存在系统中,如果不存在提示出错
if (inde == -1) {
System.out.println("The entered student number does not exist, please enter the correct student number");
} else {
System.out.println("Please enter the student's new name:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the student’s new age:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the student's new major:");
String major = sc.nextLine();
Student s = new Student(id, name, age, major);
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student student = arrayList.get(i);
if (student.getStu_id().equals(id)) {
arrayList.set(i, s);
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//查看系统中所有学生的信息
public static void findAllStudent(ArrayList<Student> arrayList) {
if (arrayList.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("No student information, please add student information first");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("%-15s", "student ID") + String.format("%-15s", "name") + String.format("%-15s", "age") + String.format("%-15s", "Professional"));
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Student s = arrayList.get(i);
System.out.println(String.format("%-15s", s.getStu_id()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getName()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getAge()) + String.format("%-15s", s.getStu_pro()));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1 学生管理系统界面
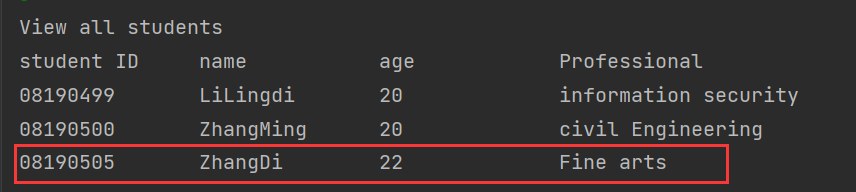
2 查看学生管理系统中所有的学生:
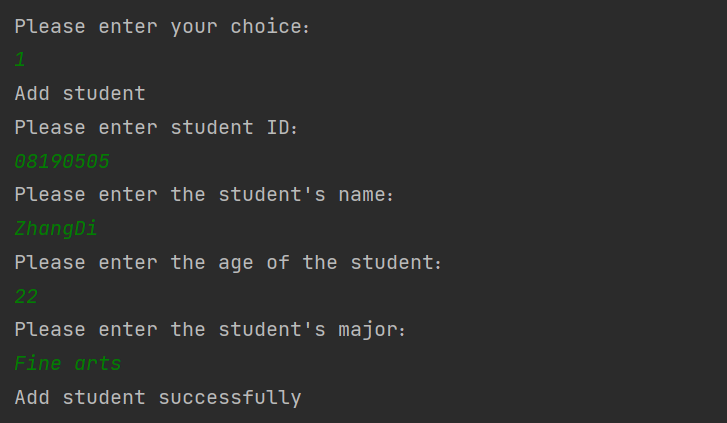
3 添加学生
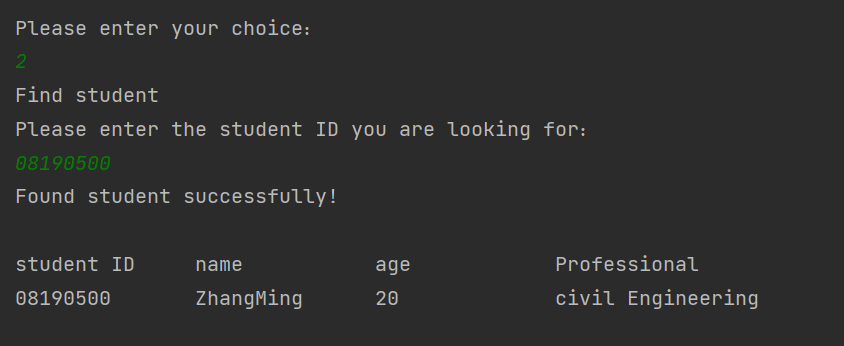
4 查找学号为08190500的学生
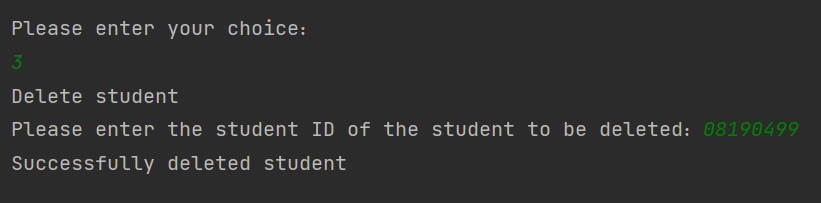
5 删除学号为08190499的学生
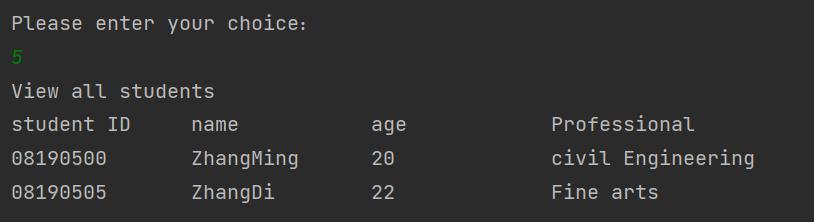
6修改学号为08190500的学生信息
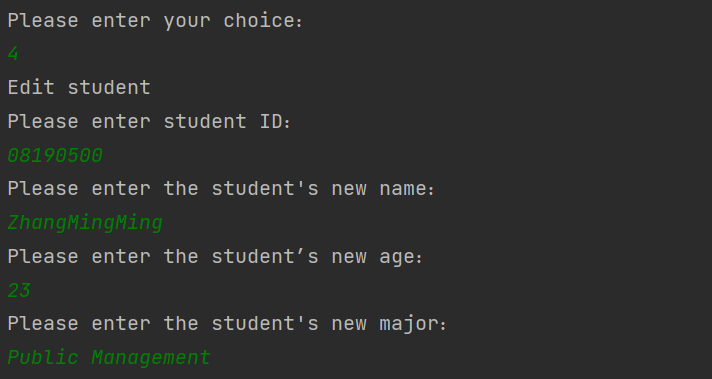
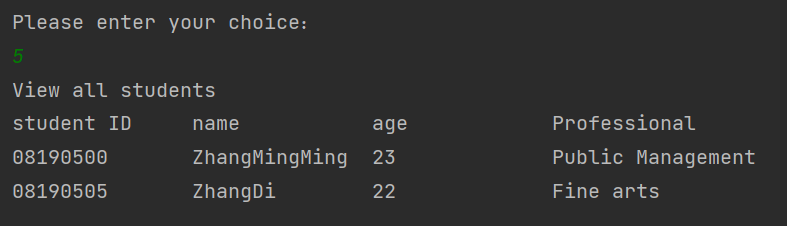
7关闭学生管理系统
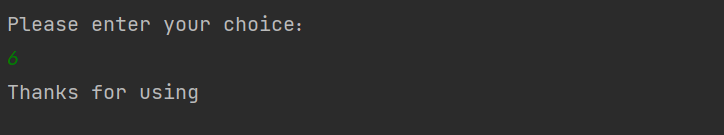
2 二元一次方程组
package quadratic;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.*;
public class qua_equation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("一元二次方程表达式为:ax^2+bx+c=0");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入方程的系数a、b、c (同时为0,终止程序):");
double a, b, c;
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
c = sc.nextDouble();
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.000000");
double flag;
double x1, x2;
flag = b * b - 4 * a * c;
if (a == 0 && b == 0 && c == 0) {
System.err.println("方程不存在");
return;
} else if (a == 0 && b != 0) {
System.err.println("此方程为一元一次方程");
double result = (-1 * c) / b;
System.out.println("方程的解为:" + tran_decimal(result));
} else if (a == 0) {
System.err.println("方程不存在");
} else if (flag == 0) {
x1 = b / -2.0 / a;
x2 = b / -2.0 / a;
System.out.println("方程有两个相同实根, x1 = "
+ df.format(x1) + ", x2 = " + df.format(x2));
} else if (flag > 0) {
x1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(flag)) / 2.0 / a;
x2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(flag)) / 2.0 / a;
System.out.println("方程有两个不同实根, x1 = "
+ df.format(x1) + ", x2 = " + df.format(x2));
} else if (flag < 0) {
double s, x;
s = -b / 2.0 / a;
x = Math.sqrt(-flag) / 2.0 / a;
System.out.println("方程有虚根, x1 = "
+ df.format(s) + " + " + df.format(x) + "i, x2 = "
+ df.format(s) + " - " + df.format(x) + "i");
}
}
}
private static BigDecimal tran_decimal(double n) {
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal(n);//将n的值赋给形参bd
return bd.setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
}
}输出结果为:
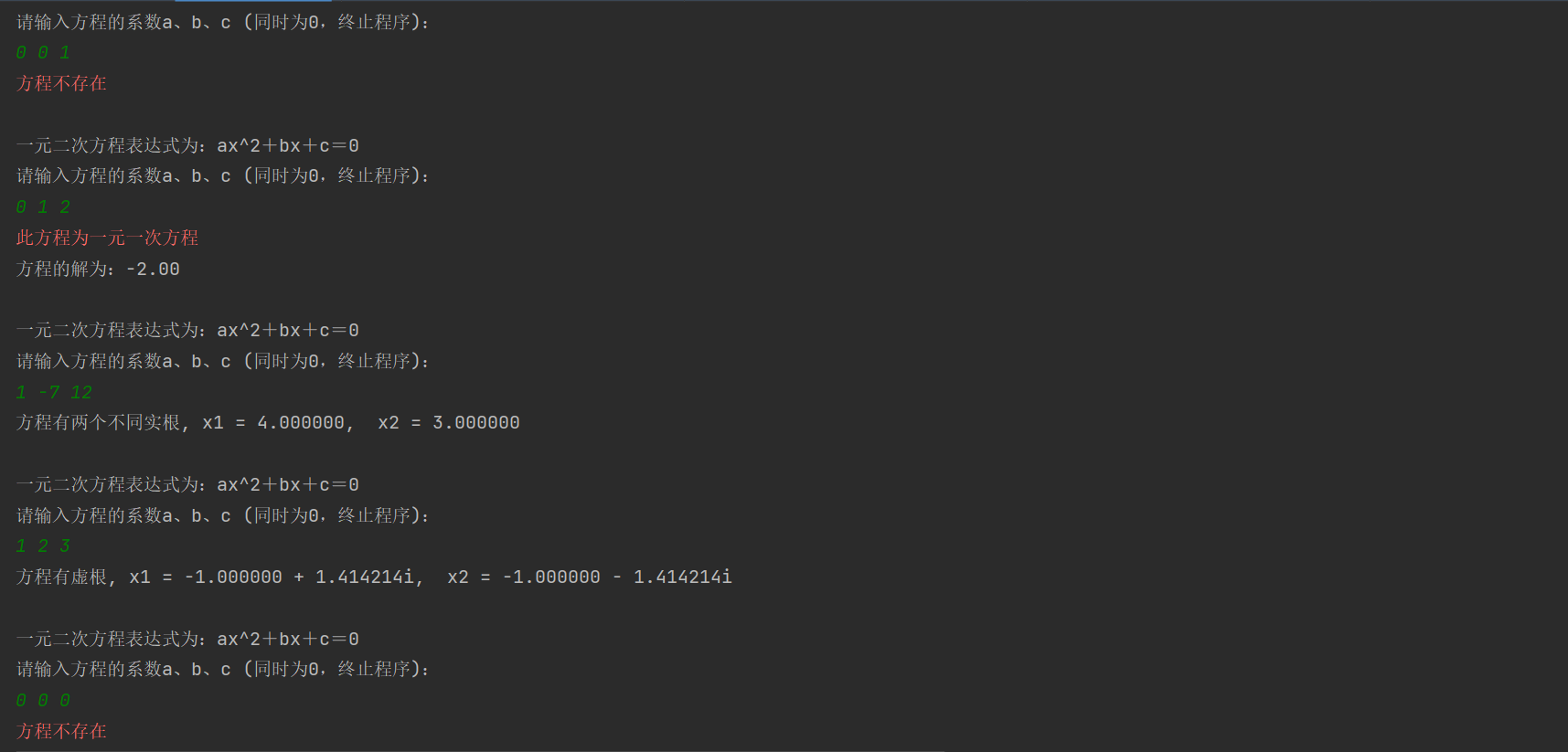
第一种情况:只有常数项:提示方程不存在。
第二种情况:x+2=0:提示方程为一元一次方程。
第三种情况:x2-7x+12=0:方程有两个不同的实根。
第四种情况:x2+2x+3=0:存在虚根。
GUI
package equation;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Panel_equ extends Panel {
static JTextField text1 = new JTextField(15);
static JTextField text2 = new JTextField(15);
static JTextField text3 = new JTextField(15);
static JButton button = new JButton("确定");
static JButton button2 = new JButton("清空");
static JButton button3 = new JButton("退出");
Panel_equ()
{
this.setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("二次项系数:");
this.add(label1);
this.add(text1);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("一次项系数:");
this.add(label2);
this.add(text2);
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("常数项:");
this.add(label3);
this.add(text3);
this.add(button);
button2.addActionListener(new Frame_equ.CustomActionListener());
this.add(button2);
button3.addActionListener(new Frame_equ.CustomActionListener2());
this.add(button3,BorderLayout.NORTH);
}
}
package equation;
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
public class Frame_equ extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
static Panel_equ panel;
static JTextArea textArea;
Calculate_equ s1;
public Frame_equ() {
this.setTitle("一元二次方程 1.0");
this.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
panel = new Panel_equ();
Panel_equ.button.addActionListener(this);
textArea = new JTextArea();
textArea.setBounds(getX(), getY(), 500, 100);
add(panel, BorderLayout.WEST);
add(textArea, BorderLayout.CENTER);
setBounds(450, 300, 600, 125);
setVisible(true);
validate();
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
s1 = new Calculate_equ(Double.parseDouble(Panel_equ.text1.getText()), Double.parseDouble(Panel_equ.text2.getText()), Double.parseDouble(Panel_equ.text3.getText()));
s1.Solve();
//序列化
try(FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("file1.data");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut))
{
out.writeObject(s1);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
//反序列化
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file1.data");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Calculate_equ temp =(Calculate_equ) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("二次项系数:"+temp.getA());
System.out.println("一次项系数:"+temp.getB());
System.out.println("常数项系数:"+temp.getC());
System.out.println("解:"+Calculate_equ.m);
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.print(e2.getMessage());
}
}catch(NumberFormatException e1){
Calculate_equ.m = "文本框没有输入内容!";
textArea.setText(Calculate_equ.m);
}catch (NoQuadratic e2){
Calculate_equ.m =e2.toString();
textArea.setText(Calculate_equ.m);
}
textArea.setText(Calculate_equ.m);
}
static class CustomActionListener implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Panel_equ.text1.setText("");
Panel_equ.text2.setText("");
Panel_equ.text3.setText("");
textArea.setText("");
}
}
static class CustomActionListener2 implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
package equation;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
//自定义异常,二次项系数为0
class NoQuadratic extends Exception {
public String mess;
public NoQuadratic() {
mess = "此方程不是一元二次方程!";
}
public String toString() {
return mess;
}
}
// A是二次方系数;B是一次放系数;C是常数项系数;x1,x2用于存储两个根;m返回信息;s是实部;x是虚部;
public class Calculate_equ implements Serializable {
private final double A;
private final double B;
private final double C;
public static String m;
public Calculate_equ(double A, double B, double C) {
this.A = A;
this.B = B;
this.C = C;
}
public double getA() {
return A;
}
public double getB() {
return B;
}
public double getC() {
return C;
}
//求解两根
public void Solve() throws NoQuadratic {
double flag = this.B * this.B - 4 * this.A * this.C;
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.000000");
if (this.A == 0) {
throw new NoQuadratic();
} else if (flag < 0) {
double s = this.B / 2.0 / this.A;
double x = Math.sqrt(-flag) / 2.0 / this.A;
m = "方程有虚根, x1 = " + df.format(s) + " + " + df.format(x) + "i, x2 = "
+ df.format(s) + " - " + df.format(x) + "i";
} else {
double x1 = ((-this.B) + Math.sqrt(flag)) / 2 * this.A;
double x2 = ((-this.B) - Math.sqrt(flag)) / 2 * this.A;
m = "方程有两个实根,x1 = " + x1 + " x2 = " + x2;
}
}
}
package equation;
public class Start_equ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Frame_equ();
}
}
图形界面:

输入一元二次方程的三个系数。
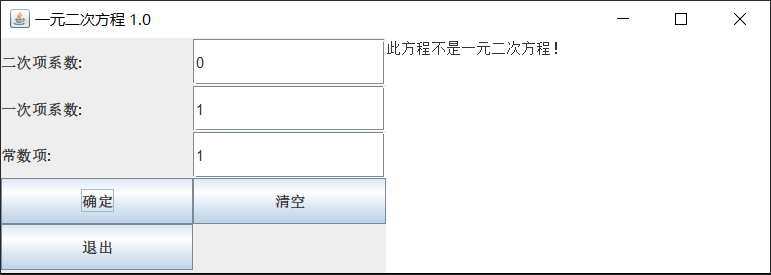
1 不是一元二次方程,抛出异常。
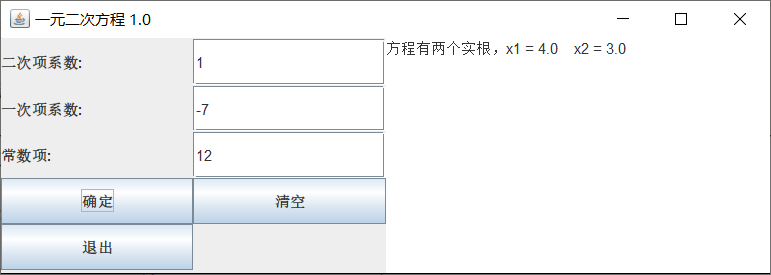
2 存在实根。
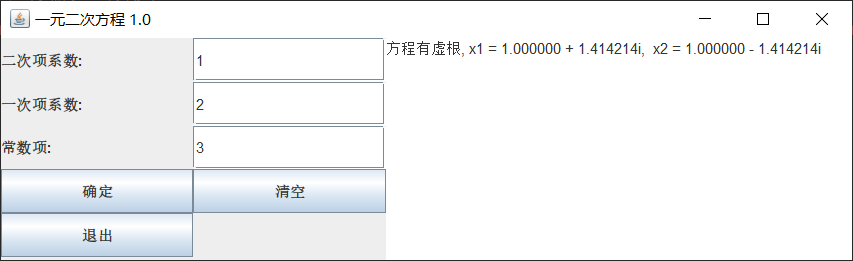
3 存在虚根。
4 清空按钮,可以看到清空按钮上有上次点击的标记,可以有效证明按钮可行。
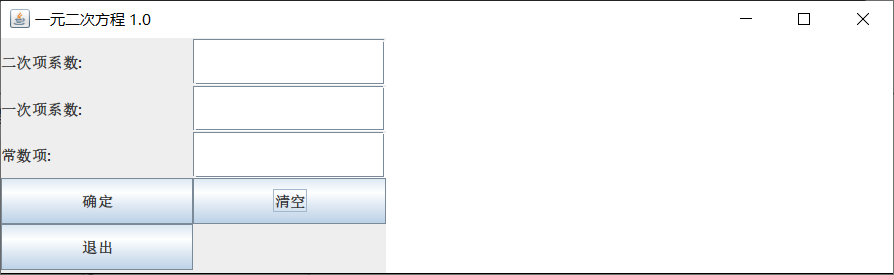
5 退出,可行。
6 把生成的一元二次方程对象(包含根的值)序列化并保存在文件file1.data中。
//序列化并保存在file.data
try(FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("file1.data");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut))
{
out.writeObject(s1);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
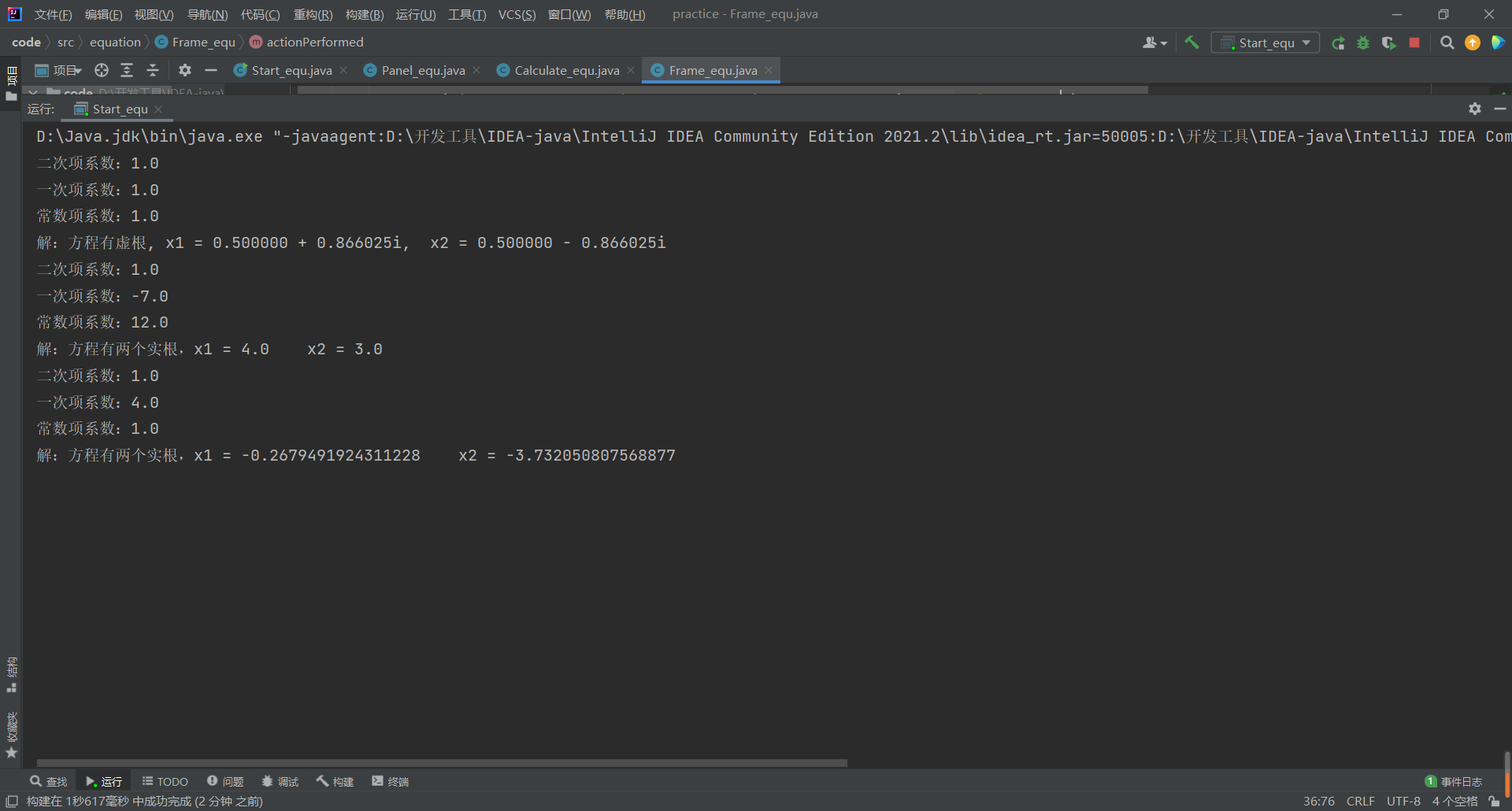
7 反序列化结果显示在命令行界面中。
//反序列化输出
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file1.data");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Calculate_equ temp =(Calculate_equ) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("二次项系数:"+temp.getA());
System.out.println("一次项系数:"+temp.getB());
System.out.println("常数项系数:"+temp.getC());
System.out.println("解:"+Calculate_equ.m);
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.print(e2.getMessage());
}
JAVA:作业四
1 正则表达式
输入三个字符串判断 满足密码复杂性要求(认证需求);满足身份证号码规范(15/18);满足电子邮件规范
判断密码的复杂性
package four_job;
public class password {
private String pwd;
public void setPsw(String psword) {
this.pwd = psword;
}
public boolean kind_Check() {
if (pwd.length() <= 8 || pwd.replaceAll("(.{3,})(?=.{3,}\\1)", "").length() < pwd.length()) {
return false;
}
// 大小写字母.数字.其它符号check
int count = 0;
if (pwd.matches(".*\\d+.*")) count++;
if (pwd.matches(".*[a-z]+.*")) count++;
if (pwd.matches(".*[A-Z]+.*")) count++;
if (pwd.matches(".*[\\p{P}\\p{S}]+.*")) count++;
if (count < 3) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
判断身份证号规范
package four_job;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class idcard {
public static final String VALIDITY = "该身份证有效!";
public static final String NUMBER = "身份证号码长度应该为15位或18位。";
public static final String DIGITS = "身份证15位号码都应为数字 ; 18位号码除最后一位外,都应为数字。";
public static final String BIRTH = "身份证出生日期无效。";
public static final String RANGE = "身份证生日不在有效范围。";
public static final String MONTH = "身份证月份无效";
public static final String DAY = "身份证日期无效";
public static final String AREA = "身份证地区编码错误。";
public static final String ILLEGAL = "不是合法的身份证号码";
public static String IDCardValidate(String IDStr) {
String tipInfo = VALIDITY;
String Ai;
// 判断号码的长度 15位或18位
if (IDStr.length() != 15 && IDStr.length() != 18) {
tipInfo = NUMBER;
return tipInfo;
}
// 18位身份证前17位位数字,如果是15位的身份证则所有号码都为数字
if (IDStr.length() == 18) {
Ai = IDStr.substring(0, 17);
} else {
Ai = IDStr.substring(0, 6) + "19" + IDStr.substring(6, 15);
}
if (!Number(Ai)) {
tipInfo = DIGITS;
return tipInfo;
}
// 判断出生年月是否有效
String strYear = Ai.substring(6, 10);
String strMonth = Ai.substring(10, 12);
String strDay = Ai.substring(12, 14);
if (!Date(strYear + "-" + strMonth + "-" + strDay)) {
tipInfo = BIRTH;
return tipInfo;
}
GregorianCalendar gc = new GregorianCalendar();
SimpleDateFormat s = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
try {
if ((gc.get(Calendar.YEAR) - Integer.parseInt(strYear)) > 150
|| (gc.getTime().getTime() - s.parse(strYear + "-" + strMonth + "-" + strDay).getTime()) < 0) {
tipInfo = RANGE;
return tipInfo;
}
} catch (NumberFormatException | ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (Integer.parseInt(strMonth) > 12 || Integer.parseInt(strMonth) == 0) {
tipInfo = MONTH;
return tipInfo;
}
if (Integer.parseInt(strDay) > 31 || Integer.parseInt(strDay) == 0) {
tipInfo = DAY;
return tipInfo;
}
// 判断地区码是否有效
Hashtable<String, String> areacode = Area();
// 如果身份证前两位的地区码不在Hashtable,则地区码有误
if (areacode.get(Ai.substring(0, 2)) == null) {
tipInfo = AREA;
return tipInfo;
}
if (!Varycode(Ai, IDStr)) {
tipInfo = ILLEGAL;
return tipInfo;
}
return tipInfo;
}
//对第18位进行校验
private static boolean Varycode(String Ai, String IDStr) {
String[] VarifyCode = {"1", "0", "X", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3", "2"};
String[] Wi = {"7", "9", "10", "5", "8", "4", "2", "1", "6", "3", "7", "9", "10", "5", "8", "4", "2"};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 17; i++) {
sum = sum + Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(Ai.charAt(i))) * Integer.parseInt(Wi[i]);
}
int modValue = sum % 11;
String strVerifyCode = VarifyCode[modValue];
Ai = Ai + strVerifyCode;
if (IDStr.length() == 18) {
return Ai.equals(IDStr);
}
return true;
}
//判断字符串是否位数字
private static boolean Number(String strnum) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]*");
Matcher isNum = pattern.matcher(strnum);
return isNum.matches();
}
//判断出生日期是否正确
public static boolean Date(String strDate) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(
"^((\\d{2}(([02468][048])|([13579][26]))[\\-\\/\\s]?((((0?[13578])|(1[02]))[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|([1-2][0-9])|(3[01])))|(((0?[469])|(11))[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|([1-2][0-9])|(30)))|(0?2[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|([1-2][0-9])))))|(\\d{2}(([02468][1235679])|([13579][01345789]))[\\-\\/\\s]?((((0?[13578])|(1[02]))[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|([1-2][0-9])|(3[01])))|(((0?[469])|(11))[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|([1-2][0-9])|(30)))|(0?2[\\-\\/\\s]?((0?[1-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-8]))))))?$");
Matcher m = pattern.matcher(strDate);
return m.matches();
}
//判断身份证上的地址是否正确
private static Hashtable<String, String> Area() {
Hashtable<String, String> h = new Hashtable<>();
h.put("11", "北京");
h.put("12", "天津");
h.put("13", "河北");
h.put("14", "山西");
h.put("15", "内蒙古");
h.put("21", "辽宁");
h.put("22", "吉林");
h.put("23", "黑龙江");
h.put("31", "上海");
h.put("32", "江苏");
h.put("33", "浙江");
h.put("34", "安徽");
h.put("35", "福建");
h.put("36", "江西");
h.put("37", "山东");
h.put("41", "河南");
h.put("42", "湖北");
h.put("43", "湖南");
h.put("44", "广东");
h.put("45", "广西");
h.put("46", "海南");
h.put("50", "重庆");
h.put("51", "四川");
h.put("52", "贵州");
h.put("53", "云南");
h.put("54", "西藏");
h.put("61", "陕西");
h.put("62", "甘肃");
h.put("63", "青海");
h.put("64", "宁夏");
h.put("65", "新疆");
h.put("71", "台湾");
h.put("81", "香港");
h.put("82", "澳门");
h.put("91", "国外");
return h;
}
}
判断电子邮件的规范性
@左边的限制:
- 由a~z的英文字母(不区分大小写)开头
- 可由英文字母、0~9的数字、点、减号或下划线组成
- 长度为3~18个字符
- 不能以点、减号结尾
@右边的限制:
- 只能有一个点,点和”@”之间不能为空
- 可由英文字母、0~9的数字、点、减号或下划线组成
- 不能以点、减号或下划线结尾
package four_job;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class email {
private String emaill;
public void set_email(String new_emil) {
this.emaill = new_emil;
}
public boolean isValidEmail() {
if ((this.emaill != null) && (!this.emaill.isEmpty())) {
return Pattern.matches("^(\\w+([-.][A-Za-z0-9]+)*){3,18}@\\w+([-.][A-Za-z0-9]+)*\\.\\w+([-.][A-Za-z0-9]+)*$", this.emaill);
}
return false;
}
}正确性验证:
package four_job;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class four_one {
public static void test() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
password psw = new password();
email obj_email = new email();
while (true) {
System.out.println("请选择:\n[P]密码复杂性判断 [I]身份证号码规范判断 [E]电子邮件规范判断 [Q]终止");
char type = scan.next().charAt(0);
if (type == 'P' || type == 'p') {
Scanner scan_one = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String psword = scan_one.nextLine();
psw.setPsw(psword);
if (psw.kind_Check())
System.out.println("满足密码复杂性要求");
else
System.out.println("不满足密码复杂性要求!");
}else if (type == 'I' || type == 'i') {
Scanner scan_three = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入身份证号:");
String IdCard = scan_three.next();
System.out.println(idcard.IDCardValidate(IdCard));
}
else if (type == 'E' || type == 'e') {
Scanner scan_two = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入电子邮件:");
String new_email = scan_two.nextLine();
obj_email.set_email(new_email);
if (obj_email.isValidEmail())
System.out.println("电子邮件规范");
else
System.out.println("电子邮件不规范!");
} else if (type == 'Q' || type == 'q') {
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
}
密码复杂性验证
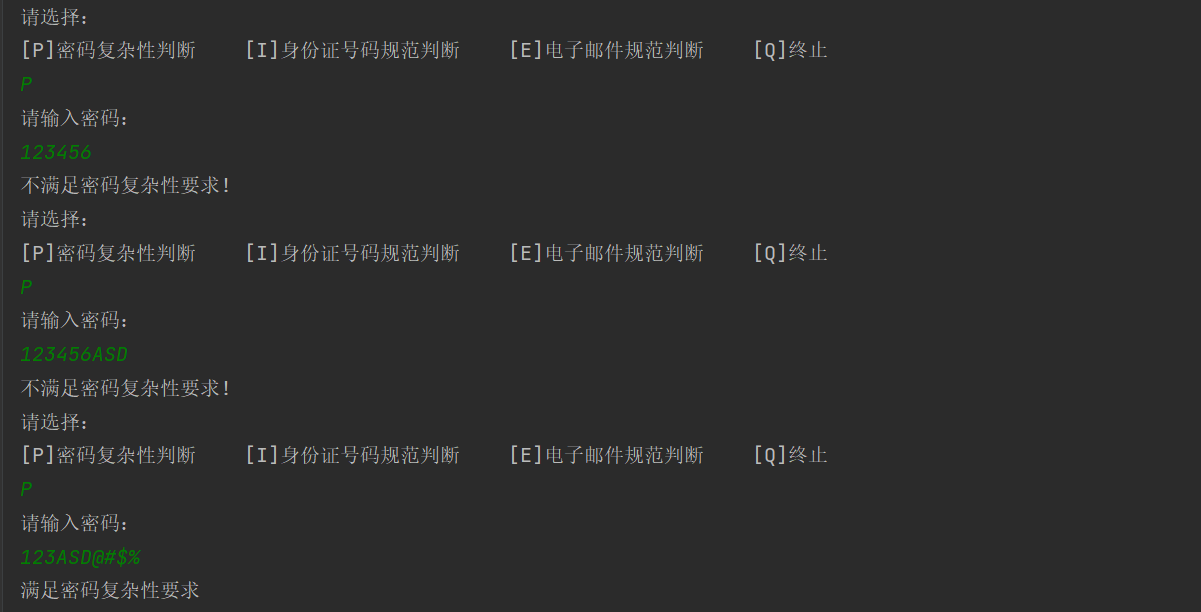
身份证号规范性验证
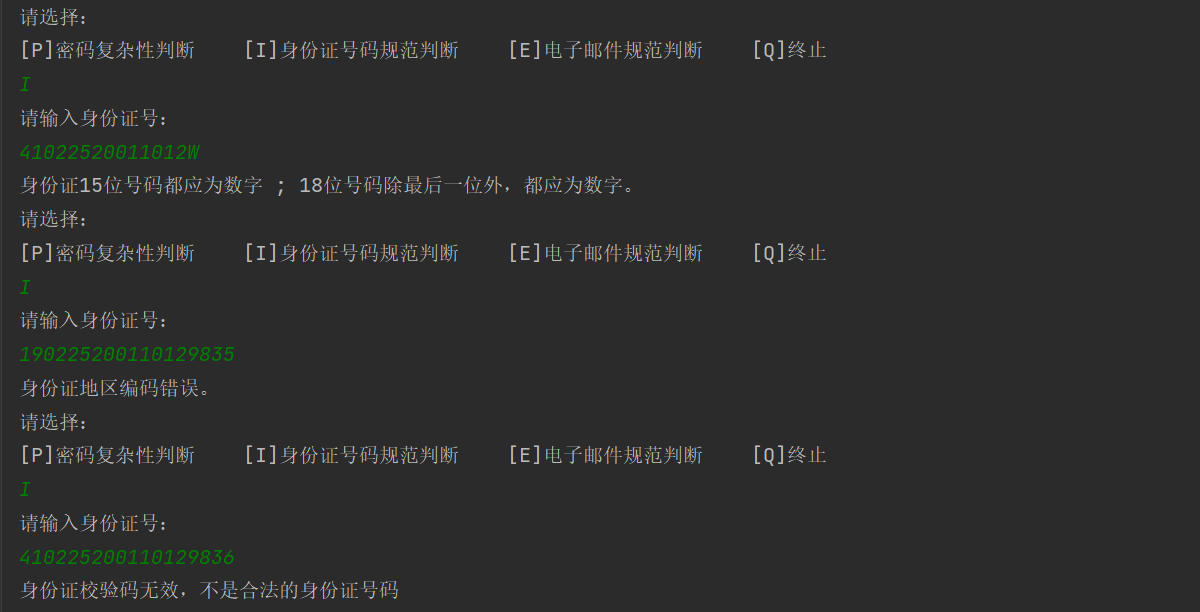

电子邮件规范验证

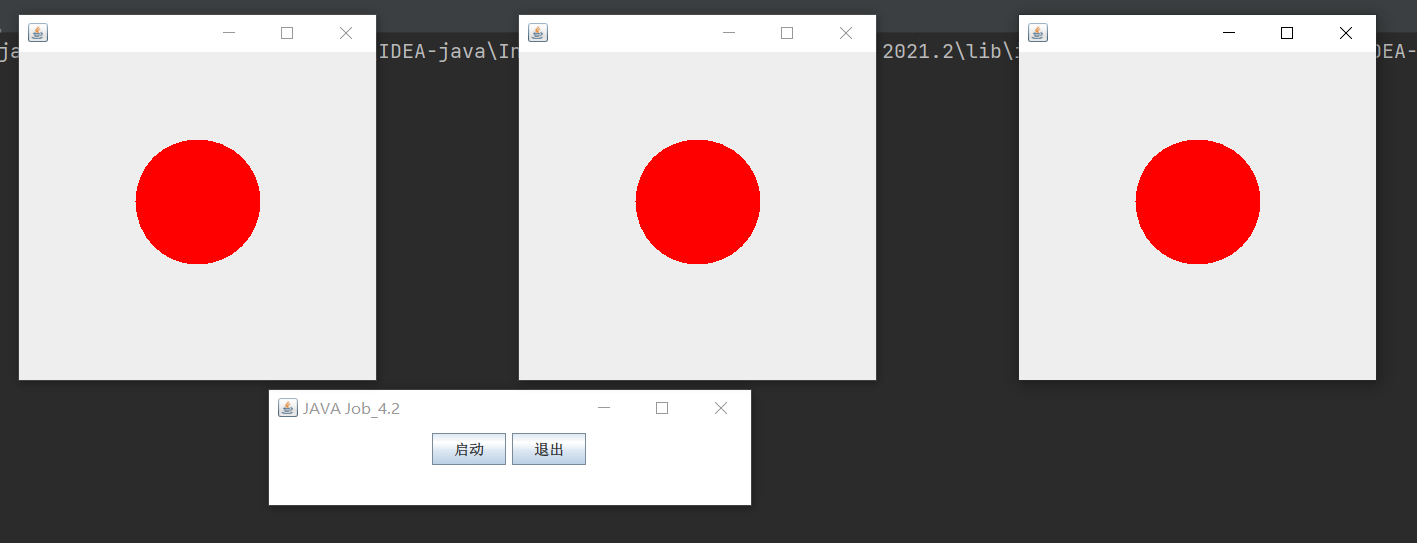
2 绘制动态图形
利用鼠标事件启动3个线程分别在三个窗口中同时绘制动态图形
package four_job;
import equation.Frame_equ;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class even_mouse extends JFrame implements Runnable {
int i = 0;
Thread t;
public even_mouse() {
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
t = new Thread(this);
t.start();
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
try {
repaint();
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (
Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
super.paint(g);
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.fillOval(50 + i * 10, 50 + i * 10, 100, 100);
}
public static void main(String arg[]) {
// 创建窗体对象
Frame f = new Frame("JAVA Job_4.2");
f.setSize(400, 100);
f.setLocation(400, 400);
//更改布局方式
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 创建按钮对象
JButton bu = new JButton("启动");
JButton button = new JButton("退出");
// 设置按钮大小
bu.setSize(20, 10);
button.setSize(20, 10);
// 把按钮添加到窗体
f.add(bu);
f.add(button);
// 给窗体加一个关闭事件
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
//给按钮添加一个事件
//ActionListener动作监听
bu.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
even_mouse my = new even_mouse();
even_mouse my_two = new even_mouse();
even_mouse my_three = new even_mouse();
my.setBounds(200, 100, 300, 300);
my_two.setBounds(600, 100, 300, 300);
my_three.setBounds(1000, 100, 300, 300);
my.setVisible(true);
my_two.setVisible(true);
my_three.setVisible(true);
}
});
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
f.setVisible(true);
}
}效果演示: